一、安装 libfuse。在 Ubuntu 中打开终端并使用以下命令安装 FUSE 库支持:
sudo apt install libfuse2二、确保 AppImage 文件具有正确的文件权限。需要对下载的应用的 AppImage 文件具有“执行”权限。转到你已下载所需应用的 AppImage 文件的文件夹。右键单击并选择“属性”。现在转到权限选项卡并选中“允许将文件作为程序执行”选项。
三、设置完成后只需双击该文件,它就会按预期运行应用。
群而不党,和而不同,自由理性皆容纳
一、安装 libfuse。在 Ubuntu 中打开终端并使用以下命令安装 FUSE 库支持:
sudo apt install libfuse2二、确保 AppImage 文件具有正确的文件权限。需要对下载的应用的 AppImage 文件具有“执行”权限。转到你已下载所需应用的 AppImage 文件的文件夹。右键单击并选择“属性”。现在转到权限选项卡并选中“允许将文件作为程序执行”选项。
三、设置完成后只需双击该文件,它就会按预期运行应用。
第一次安装v2rayA后,发现无法访问 UI 界面,原来安装完毕后 v2rayA 默认不会设置开机自动启动,需要手动启动相关服务,执行命令:
systemctl enable --now v2raya.service
升级安装也不会自动重启正在运行的 v2rayA ,需要重启已经运行的 v2rayA,执行命令:
systemctl restart v2raya.service
执行以上命令后,现在可以进入v2rayA登陆UI界面了。在第一次进入页面时,你需要创建一个管理员账号,请妥善保管你的用户名密码,如果遗忘,使用sudo v2raya --reset-password命令重置。
然后继续使用v2rayA时,又弹出提示:
检测到 geosite.dat, geoip.dat 文件或 v2ray-core 可能未正确安装,请检查
解决思路为下载安装v2ray/xray core。
v2ray core: https://github.com/v2fly/v2ray-core
xray core: https://github.com/XTLS/Xray-core
可以在上面任何一个网趾下载安装文件,下载的时候需要注意你的 CPU 架构,下载好之后解开压缩包,然后把可执行文件复制到 /usr/local/bin/ 或 /usr/bin/(推荐前者),把几个 dat 格式的文件复制到 /usr/local/share/v2ray/ 或者 /usr/share/v2ray/(推荐前者,xray 用户记得把文件放到 xray 文件夹),最后授予 v2ray/xray 可执行权限。
以下是用 bash 命令操作的示例(假设命令在 root 用户下运行):
wget https://github.com/v2fly/v2ray-core/releases/latest/download/v2ray-linux-64.zip
unzip v2ray-linux-64.zip -d ./v2ray
sudo mkdir -p /usr/local/share/v2ray
sudo cp ./v2ray/*dat /usr/local/share/v2ray
sudo install -Dm755 ./v2ray/v2ray /usr/local/bin/v2ray详细操作命令的步骤如下:
taiji@debian:~/下载$ wget https://github.com/v2fly/v2ray-core/releases/latest/download/v2ray-linux-64.zip
--2023-12-02 09:41:22-- https://github.com/v2fly/v2ray-core/releases/latest/download/v2ray-linux-64.zip
正在解析主机 github.com (github.com)... 20.205.243.166
正在连接 github.com (github.com)|20.205.243.166|:443... 已连接。已发出 HTTP 请求,正在等待回应... 302 Found
位置:https://github.com/v2fly/v2ray-core/releases/download/v5.12.1/v2ray-linux-64.zip [跟随至新的 URL]
--2023-12-02 09:41:24-- https://github.com/v2fly/v2ray-core/releases/download/v5.12.1/v2ray-linux-64.zip
再次使用存在的到 github.com:443 的连接。已发出 HTTP 请求,正在等待回应... 302 Found
位置:https://objects.githubusercontent.com/github-production-release-asset-2e65be/181461073/e1381378-51d2-41b8-a6a0-3d26708cb36b?X-Amz-Algorithm=AWS4-HMAC-SHA256&X-Amz-Credential=AKIAIWNJYAX4CSVEH53A%2F20231202%2Fus-east-1%2Fs3%2Faws4_request&X-Amz-Date=20231202T013928Z&X-Amz-Expires=300&X-Amz-Signature=1329b32bbc67ba00916300f8407cbf7f3846572e283b4ab0270e4c466e048b3c&X-Amz-SignedHeaders=host&actor_id=0&key_id=0&repo_id=181461073&response-content-disposition=attachment%3B%20filename%3Dv2ray-linux-64.zip&response-content-type=application%2Foctet-stream [跟随至新的 URL]
--2023-12-02 09:41:25-- https://objects.githubusercontent.com/github-production-release-asset-2e65be/181461073/e1381378-51d2-41b8-a6a0-3d26708cb36b?X-Amz-Algorithm=AWS4-HMAC-SHA256&X-Amz-Credential=AKIAIWNJYAX4CSVEH53A%2F20231202%2Fus-east-1%2Fs3%2Faws4_request&X-Amz-Date=20231202T013928Z&X-Amz-Expires=300&X-Amz-Signature=1329b32bbc67ba00916300f8407cbf7f3846572e283b4ab0270e4c466e048b3c&X-Amz-SignedHeaders=host&actor_id=0&key_id=0&repo_id=181461073&response-content-disposition=attachment%3B%20filename%3Dv2ray-linux-64.zip&response-content-type=application%2Foctet-stream
正在解析主机 objects.githubusercontent.com (objects.githubusercontent.com)... 185.199.109.133, 185.199.111.133, 185.199.110.133, ...
正在连接 objects.githubusercontent.com (objects.githubusercontent.com)|185.199.109.133|:443... 已连接。已发出 HTTP 请求,正在等待回应... 200 OK
长度:14411930 (14M) [application/octet-stream]
正在保存至: “v2ray-linux-64.zip”
v2ray-linux-64.zip 100%[=========================================>] 13.74M 18.9MB/s 用时 0.7s
2023-12-02 09:41:28 (18.9 MB/s) - 已保存 “v2ray-linux-64.zip” [14411930/14411930])
taiji@debian:~/下载$ unzip v2ray-linux-64.zip -d ./v2ray
Archive: v2ray-linux-64.zip
inflating: ./v2ray/config.json
inflating: ./v2ray/geoip-only-cn-private.dat
inflating: ./v2ray/vpoint_vmess_freedom.json
inflating: ./v2ray/geoip.dat
inflating: ./v2ray/vpoint_socks_vmess.json
inflating: ./v2ray/v2ray
inflating: ./v2ray/geosite.dat
creating: ./v2ray/systemd/
creating: ./v2ray/systemd/system/
inflating: ./v2ray/systemd/system/v2ray.service
inflating: ./v2ray/systemd/system/v2ray@.service
taiji@debian:~/下载$ sudo mkdir -p /usr/local/share/v2ray
[sudo] taiji 的密码:
taiji 不是 sudoers 文件。
taiji@debian:~/下载$ su
密码:
root@debian:/home/taiji/下载# sudo mkdir -p /usr/local/share/v2ray
root@debian:/home/taiji/下载# sudo cp ./v2ray/*dat /usr/local/share/v2ray
root@debian:/home/taiji/下载# sudo install -Dm755 ./v2ray/v2ray /usr/local/bin/v2ray
root@debian:/home/taiji/下载#
操作完以上步骤后,再打开v2rayA时,就可以正常使用了!
本人目前使用Debian+Ubuntu作为主力系统,家里的两台电脑装了三个系统。其中新台式机安装的两个系统,分别是使用Gnome为桌面环境的Ubuntu和传统的Win 11系统;老台式机装了两个分别以Dde和Gnome为桌面环境的Debian系统。以前是以Debian的DDE桌面环境为主力系统,但是经过最近对Ubuntu的一番折腾后发现Gnome还是挺好用的,于是将老台式机其中一个硬盘上的Debian系统也安装了Gnome桌面环境。安装倒是很简单,后来发现新安装的Gnome桌面环境不怎么好驾驭,因为它只是一个基本的桌面环境,很多功能都没有,光秃秃的。于是动手对Gnome桌面环境进行DIY改造,现在总结和分享一下Gnome桌面环境必装的几个插件。
一、Desktop Icons
新版本的Gnome不能再往桌面创建桌面图标了,若需要桌面图标,推荐这款插件,用以正常显示桌面图标。
二、Hide Top Bar
安装好了插件以后进行设置,就可以用来智能隐藏顶栏,我是设置为鼠标碰屏幕上方时,显示顶栏,当全屏浏览器和文件夹时,顶栏自动隐藏,这样可以增大纵向的可读面积。
三、Dash to Dock
老牌插件了,相信这款插件各位都很熟悉,该插件提供了一个类似于Mac的Dock的功能,用以在下方显示任务栏。
四、Tray Icons
新版的Gnome居然把托盘都给取消了,这骚操作过于迷惑,也不知道开发者怎么想的,这款插件用于显示顶栏右方的托盘图标。
五、Transparent Topbar
你可能对Gnome默认那黑乎乎的顶栏感到非常丑,装上这个插件让你的顶栏变得透明,这样桌面是不是就好看了一分呢?
六、gnome tweak(优化)
原始的Gnome在打开浏览器和文件夹时在标题栏右边只显示了一个关闭按钮,不能显示“最大化”和“最小化”按钮。装上这个插件之后,就可以显示“最大化”和“最小化”按钮了。
七、Dash to Panel(windows任务栏效果)
原始的Gnome系统界面在上面和左侧各有一个状态栏,安装这个插件之后,可以将状态栏调整为和windows任务栏一样的视觉效果。
八、Lunar Calendar (农历)
需要先安装两个文件包,否则在安装插件时报错:
http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/pool/universe/l/lunar-date/liblunar-date-2.0-0_2.4.0-5_amd64.deb
http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/pool/universe/l/lunar-date/gir1.2-lunar-date-2.0_2.4.0-5_amd64.deb
下载并安装这两个文件包后,就可以正常安装Lunar Calendar了。
九、OpenWeather Refined(天气)
可以在顶栏安排天气插件,随时察看天气。这个插件具有灵活的定制功能,非常酷。
另外,刚才忘记说如何安装插件了。我们在linux系统中用Firefox浏览器打开Gnome的官方网站 https://extensions.gnome.org/(如果用chrome浏览器打开,则需要先安装连接器,执行命令“sudo apt install chrome-gnome-shell”),然后分别输入以上插件名称进行搜索,搜索到了之后,在页面标题的右边有个插件开关按钮,打开开关之后,一会儿会弹出安装的提示,直接安装就可以。安装完插件之后,刷新当前页面,可以看到在页面标题右边的开关按钮旁边,会出现一个设置的按钮,打开进行设置就可以了。
Ubuntu 系统的 Dock图标默认点击时只会显示,而再次点击不会最小化。可使用gsetting命令启用点击最小化功能。
gsettings set org.gnome.shell.extensions.dash-to-dock click-action 'minimize'再次点击Dock图标即可实现最小化。
gsettings reset org.gnome.shell.extensions.dash-to-dock click-actiongsettings range org.gnome.shell.extensions.dash-to-dock click-actionUbuntu 22.04 还有如下选项可供选择,自己可以试一试哪个最适合自己。
'skip'
'minimize'
'launch'
'cycle-windows'
'minimize-or-overview'
'previews'
'minimize-or-previews'
'focus-or-previews'
'focus-minimize-or-previews'
'quit'gsettings set org.gnome.shell.extensions.dash-to-dock click-action 'minimize-or-previews'如图标下只有一个窗口,则显示或最小化窗口。
如图标下有多个窗口则会显示多个窗口的预览,再选择需要的窗口打开。
首先检查有没有安装 debtap:
sudo pacman -Q debtap
没有就先安装:
yaourt -S debtap
然后升级debtap:
sudo debtap -u
安装deb包的方法:
sudo debtap xxxx.deb
安装时会提示输入包名,以及license。包名随意,license就填GPL吧!
上述操作完成后会在deb包同级目录生成×.tar.xz文件,直接用pacman安装即可:
sudo pacman -U x.tar.xz
搜索包:
pacman -Ss 关键字:在仓库中搜索含关键字的包。
pacman -Qs 关键字: 搜索已安装的包。
pacman -Qi 包名:查看有关包的详尽信息。
pacman -Ql 包名:列出该包的文件。
安装软件包:
sudo pacman -S package_name或sudo pacman -Sy package_name
yay -S package_name(若要使用yay,先安装,安装方法 sudo pacman -S yay)
删除单个软件包,保留其全部已经安装的依赖关系
sudo pacman -R package_name
删除指定软件包,及其所有没有被其他已安装软件包使用的依赖关系:
sudo pacman -Rs package_name
要删除软件包和所有依赖这个软件包的程序:
sudo pacman -Rsc package_name
警告: 此操作是递归的,请小心检查,可能会一次删除大量的软件包。
要删除软件包,但是不删除依赖这个软件包的其他程序:
sudo pacman -Rdd package_name
sudo pacman 删除某些程序时会备份重要配置文件,在其后面加上*.pacsave扩展名。-n 选项可以删除这些文件:
sudo pacman -Rn package_name
sudo pacman -Rsn package_name
Linux Mint系统用了二个月,觉得着还可以。但因为安卓手机连接系统时报错的问题,就想尝试着把系统内核升级一下,以解决安卓手机连接系统时报错的问题。解决思路:使用 dpkg 手动方式升级 Linux 内核。
一、到https://kernel.ubuntu.com/~kernel-ppa/mainline/网站手动下载可用的最新 Linux 内核。
二、点击你所选择的 Linux 内核版本链接,找到你对应的架构的那部分。我的电脑CPU是amd64的,就选“Test amd64/build succeeded”那个版本,然后逐个下载内核文件到一个专门的文件夹。
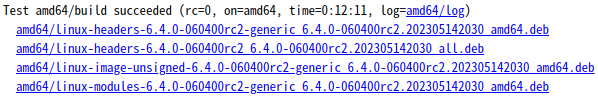
三、打开下载的文件夹,右键选择“在终端中打开”,然后执行安装命令:
sudo dpkg -i *.deb四、安装完毕后,重启系统,使用新内核:
sudo reboot五、检查是否如你所愿:
taiji@taiji:~$ uname -r
6.4.0-060400rc2-generic操作完以上步骤后,再用安卓手机连接Linux Mint系统,发现可以通过系统操作手机的存储文件了。所以解决问题的思路很重要,尝试也很重要。马云说人最大的错误是害怕犯错,有时候我们不妨大胆地去尝试一下,说不定会有意料不到的惊喜。
先删除fcitx4软件包:
sudo pacman -Rs $(pacman -Qsq fcitx)Fcitx5 安装:
复制粘贴命令:
sudo pacman -S fcitx5
sudo pacman -S fcitx5-configtool
sudo pacman -S fcitx5-qt
sudo pacman -S fcitx5-gtk
sudo pacman -S fcitx5-chinese-addons
sudo pacman -S fcitx5-material-color
sudo pacman -S kcm-fcitx5
sudo pacman -S fcitx5-luaNano(文件管理器)安装:
sudo pacman -S nano
使用方法:
保存——Ctrl + O
退出——Ctrl + X
确定——Enter
接下来用得到;修改环境变量(调用Fctix5输入法):
sudo nano /etc/environment
复制粘贴代码:
GTK_IM_MODULE=fcitx
QT_IM_MODULE=fcitx
XMODIFIERS=@im=fcitx
按照上面讲的方法进行保存,确定,退出;
重启:
rebootRootkit是一个特殊的恶意软件,它可隐藏自身以及指定的文件、进程、网络、链接、端口等信息。Rootkit可通过加载特殊的驱动修改系统内核,进而达到隐藏信息的目的。
Rootkit的三要素就是:隐藏、操纵、收集数据。不同的操作系统会有不同的Rootkit,Linux系统中的Rootkit就被称为LinuxRootkit。
Rootkit具有隐身功能,无论静止时作为文件存在,还是活动时作为进程存在,都不会被察觉,它可能永远存在于计算机中。
无论是那种形式的Rootkit,都需要实现以下功能:
1,远程指令执行
通过网络向Rootkit所驻留的系统发送指令,从而控制远程主机;
2,信息收集
收集系统的活动信息、网络上其它主机的数据信息等;
3,文件隐藏
把目标主机上的特定文件隐藏起来,使其不能通过常规方法查看到,这样就可以隐藏一部分系统被控制的痕迹;
4,进程隐藏
在控制目标主机或收集系统信息时会启动相关的进程,通过Rootkit可以实现对进程的隐藏;
5,网络连接隐藏
将网络连接的端口信息隐藏,利用netstat等工具无法显示隐藏的信息,这样就可以隐秘地向远端发送信息;
6,内核模块隐藏
将Rootkit自身在系统中安装的模块隐藏起来,提高自身生存能力。
Chkrootkit是一种Linux后门入侵检测工具,可以用来检测rootkit后门的工具,rootkit常被入侵者用来入侵控制别人的电脑,危险性很强。而,Chkrootkit工具可以很好的检测到rootkit程序。Chkrootkit运行环境为linux,可以直接通过ftp://chkrootkit.org/pub/seg/pac/chkrootkit.tar.gz地址来下载。
┌──(taiji㉿kali)-[~]
└─$ wget ftp://chkrootkit.org/pub/seg/pac/chkrootkit.tar.gz
--2023-02-10 15:15:31-- ftp://chkrootkit.org/pub/seg/pac/chkrootkit.tar.gz
=> “chkrootkit.tar.gz”
正在解析主机 chkrootkit.org (chkrootkit.org)... 187.33.4.179
正在连接 chkrootkit.org (chkrootkit.org)|187.33.4.179|:21... 已连接。正在以 anonymous 登录 ... 登录成功!==> SYST ... 完成。 ==> PWD ... 完成。==> TYPE I ... 完成。 ==> CWD (1) /pub/seg/pac ... 完成。==> SIZE chkrootkit.tar.gz ... 41948
==> PASV ... 完成。 ==> RETR chkrootkit.tar.gz ... 完成。长度:41948 (41K) (非正式数据)
chkrootkit.tar.gz 100%[=========================================>] 40.96K 39.8KB/s 用时 1.0s
2023-02-10 15:15:43 (39.8 KB/s) - “chkrootkit.tar.gz” 已保存 [41948]随后进行解压缩:
┌──(taiji㉿kali)-[~]
└─$ tar zxvf chkrootkit.tar.gz
chkrootkit-0.57/ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
chkrootkit-0.57/check_wtmpx.c
chkrootkit-0.57/chkdirs.c
chkrootkit-0.57/chklastlog.c
chkrootkit-0.57/chkproc.c
chkrootkit-0.57/chkrootkit
chkrootkit-0.57/chkrootkit.lsm
chkrootkit-0.57/chkutmp.c
chkrootkit-0.57/chkwtmp.c
chkrootkit-0.57/COPYRIGHT
chkrootkit-0.57/ifpromisc.c
chkrootkit-0.57/Makefile
chkrootkit-0.57/README
chkrootkit-0.57/README.chklastlog
chkrootkit-0.57/README.chkwtmp
chkrootkit-0.57/strings.c
打开文件夹,输入make命令进行编译:
┌──(taiji㉿kali)-[~]
└─$ cd chkrootkit-*
┌──(taiji㉿kali)-[~/chkrootkit-0.57]
└─$ make
cc -DHAVE_LASTLOG_H -o chklastlog chklastlog.c
chklastlog.c: In function ‘main’:
chklastlog.c:112:9: warning: ‘memcpy’ reading 127 bytes from a region of size 14 [-Wstringop-overread]
112 | memcpy(wtmpfile, WTMP_FILENAME, 127);
| ^~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
chklastlog.c:113:9: warning: ‘memcpy’ reading 127 bytes from a region of size 17 [-Wstringop-overread]
113 | memcpy(lastlogfile, LASTLOG_FILENAME, 127);
| ^~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
cc -DHAVE_LASTLOG_H -o chkwtmp chkwtmp.c
chkwtmp.c: In function ‘main’:
chkwtmp.c:73:8: warning: ‘memcpy’ reading 127 bytes from a region of size 14 [-Wstringop-overread]
73 | memcpy(wtmpfile, WTMP_FILENAME, 127);
| ^~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
cc -DHAVE_LASTLOG_H -D_FILE_OFFSET_BITS=64 -o ifpromisc ifpromisc.c
cc -o chkproc chkproc.c
cc -o chkdirs chkdirs.c
cc -o check_wtmpx check_wtmpx.c
cc -static -o strings-static strings.c
cc -o chkutmp chkutmp.c直接运行其chkrootkit可执行文件即可,它会对系统进行全面的rootkit检测:
┌──(taiji㉿kali)-[~/chkrootkit-0.57]
└─$ sudo ./chkrootkit
[sudo] taiji 的密码:ROOTDIR is `/'
Checking `amd'... not found
Checking `basename'... not infected
Checking `biff'... not found
Checking `chfn'... not infected
Checking `chsh'... not infected
Checking `cron'... not infected
Checking `crontab'... not infected
Checking `date'... not infected
Checking `du'... not infected
Checking `dirname'... not infected
Checking `echo'... not infected
Checking `egrep'... not infected
Checking `env'... not infected
Checking `find'... not infected上面是chkrootkit基本用法,下面再来加深些印象,首先chkrootkit可通过h参数来查看基本的帮助信息,了解其他参数及用法,如下:
┌──(taiji㉿kali)-[~/chkrootkit-0.57]
└─$ chkrootkit -h
Usage: /usr/sbin/chkrootkit [options] [test ...]
Options:
-h show this help and exit
-V show version information and exit
-l show available tests and exit
-d debug
-q quiet mode
-x expert mode
-e 'FILE1 FILE2' exclude files/dirs from results. Must be followed by a space-separated list of files/dirs.
Read /usr/share/doc/chkrootkit/README.FALSE-POSITIVES first.
-s REGEXP filter results of sniffer test through 'grep -Ev REGEXP' to exclude expected
PACKET_SNIFFERs. Read /usr/share/doc/chkrootkit/README.FALSE-POSITIVES first.
-r DIR use DIR as the root directory
-p DIR1:DIR2:DIRN path for the external commands used by chkrootkit
-n skip NFS mounted dirs示例1:chkrootkit默认检索整个系统,我们可以通过管道去搜索INFECTED(被感染)关键字,方便查看:
┌──(taiji㉿kali)-[~/chkrootkit-0.57]
└─$ ./chkrootkit | grep INFECTED
我这里是刚装的新系统,chkrootkit不应该报结果,如果有报结果,就注意查看可执行文件。
示例2:Chkrootkit也可检查系统命令是否受感染,例如ps、ls,如下
┌──(taiji㉿kali)-[~/chkrootkit-0.57]
└─$ ./chkrootkit ps ls
./chkrootkit needs root privileges
┌──(taiji㉿kali)-[~/chkrootkit-0.57]
└─$ sudo ./chkrootkit ps ls
ROOTDIR is `/'
Checking `ps'... not infected
Checking `ls'... not infected示例3:chkrootkit可传入sniffer参数来检查网络接口是否处于混杂模式,混杂模式下的网络接口会接受所有经过自己的数据流,一般管理员调试或者黑客入侵搜集信息时会用到,而正常情况下网络接口都处于非混杂模式,即只接受目标地址是自己的数据流,wireshark抓包即混杂模式接受所有数据流。
┌──(taiji㉿kali)-[~/chkrootkit-0.57]
└─$ ./chkrootkit sniffer
./chkrootkit needs root privileges
┌──(taiji㉿kali)-[~/chkrootkit-0.57]
└─$ sudo ./chkrootkit sniffer
ROOTDIR is `/'
Checking `sniffer'... eth0: PF_PACKET(/usr/sbin/NetworkManager, /usr/sbin/NetworkManager)一、首先查询网站IP,https://ipaddress.com/website/
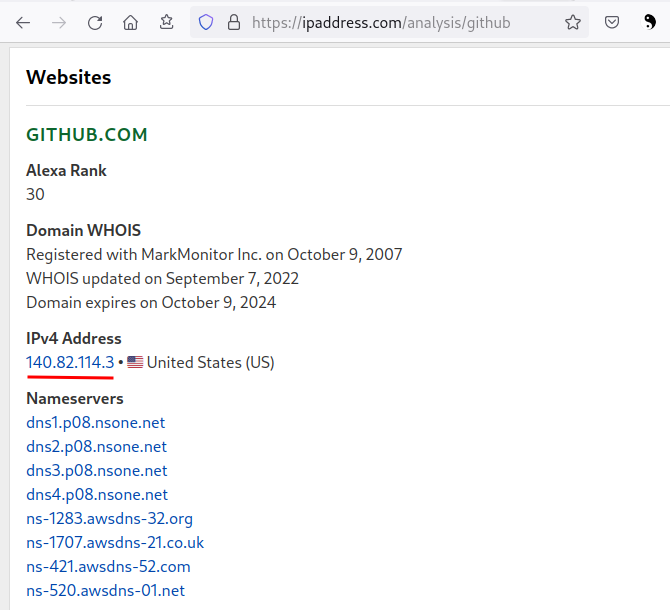
二、在windows上 C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts文件上添加:
140.82.112.4 github.com
三、在LINUX系统中,打开终端,用VIM打开hosts文件后,按“i”键编辑添加“140.82.112.4 github.com”。
┌──(taiji㉿kali)-[~]
└─$ sudo vim /etc/hosts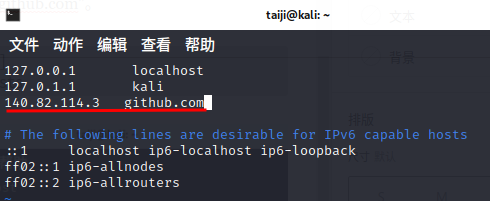
四、用VIM编辑完毕后按“ESC”键,按“SHIFT+:”,输入“wq”保存退出,再打开终端尝试,发现就可以连接下载了。
┌──(taiji㉿kali)-[~]
└─$ git clone https://github.com/RinCat/RTL88x2BU-Linux-Driver
正克隆到 'RTL88x2BU-Linux-Driver'...
remote: Enumerating objects: 2750, done.
remote: Counting objects: 100% (280/280), done.
remote: Compressing objects: 100% (73/73), done.
remote: Total 2750 (delta 241), reused 231 (delta 207), pack-reused 2470
接收对象中: 100% (2750/2750), 8.37 MiB | 99.00 KiB/s, 完成.
处理 delta 中: 100% (1964/1964), 完成.